Why Hackers Use Man in the Middle Attack
Why Hackers Use Man in the Middle Attack! In the complex realm of cybersecurity, one term that strikes fear into the hearts of both individuals and organizations is the Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack. This insidious form of cyber threat involves an attacker secretly intercepting and possibly altering the communication between two parties. In this blog post, we’ll unravel the intricacies of MITM attacks, explore how they work, and discuss effective strategies to protect against them.
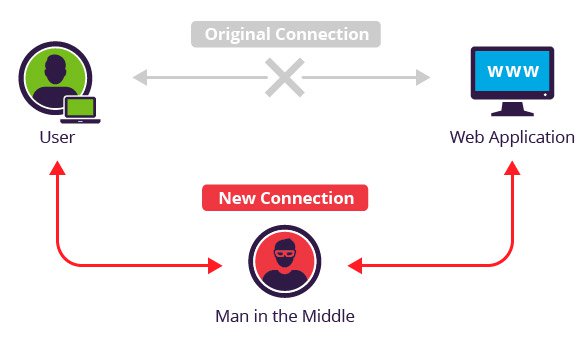
What is a Man-in-the-Middle Attack?
A Man-in-the-Middle attack occurs when a malicious actor inserts themselves into the communication between two parties, often without their knowledge. This allows the attacker to eavesdrop on, modify, or even inject new data into the communication flow.
How MITM Attacks Work:
- Interception:
- The attacker positions themselves between the two parties, intercepting the communication.
- This can happen in various scenarios, such as on unsecured Wi-Fi networks, compromised routers, or through the use of specialized software.
- Modification:
- The attacker may alter the data being transmitted. For instance, they could modify the content of emails, redirect users to malicious websites, or inject malicious code into seemingly legitimate files.
- Impersonation:
- In some cases, the attacker may impersonate one or both parties involved in the communication. This can lead to further exploitation and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Common MITM Attack Vectors:
- Wi-Fi Eavesdropping:
- Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in unsecured Wi-Fi networks to intercept data transmitted between devices and the internet.
- DNS Spoofing:
- Manipulating the Domain Name System (DNS) to redirect users to malicious websites by providing false IP addresses.
- Packet Sniffing:
- Monitoring and capturing data packets as they travel across a network, allowing the attacker to analyze or manipulate the information.
- SSL Stripping:
- Forcing a connection to use an unencrypted version, making it easier for the attacker to intercept and modify the data.
Signs of a MITM Attack:
- Unexpected Certificate Warnings:
- If users receive unexpected security certificate warnings while browsing, it could indicate a potential MITM attack.
- Unusual Network Behavior:
- Sudden slowdowns, disconnections, or unusual network activity may be signs of an ongoing MITM attack.
Protecting Against MITM Attacks:
- Use Encrypted Connections:
- Employ secure protocols like HTTPS to encrypt data in transit, making it more challenging for attackers to intercept and manipulate.
- VPN Usage:
- Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to create a secure and encrypted tunnel for internet traffic, preventing eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi networks.
- DNS Security:
- Implement DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) to authenticate DNS responses and protect against DNS spoofing.
- Regularly Update Systems:
- Keep software, operating systems, and security applications up to date to patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited in MITM attacks.
- Educate Users:
- Raise awareness among users about the risks of public Wi-Fi networks and the importance of verifying the security of websites they visit.
Conclusion:
Man-in-the-Middle attacks represent a serious threat in today’s interconnected digital landscape. By understanding the tactics employed by attackers and implementing robust security measures, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these clandestine cyber threats. Stay vigilant, prioritize cybersecurity, and together we can navigate the digital realm with greater resilience.







